Configuring Storage Pools¶
Understanding Storage Pools¶
Storage Pools are virtual entities that manage storage provisioning from the aggregated capacity of one or more RAID Groups pooled into a single construct with some QoS attributes.
Volumes are thinly provisioned, allocating capacity from the Pool only when needed. The Pool has an underlying block virtualization layer which maps virtual address space to physically allocated Pool space and manages sharing of Pool physical chunks between Volumes, Snapshots and Clones.
Snapshots and Clones consume zero capacity when they are created because they share the same data chunks as the originating Volume. Anytime you actually modify the data in the Volume, or in one of the Clones, the data chunk is copied-on-write (COW) from the source in order to apply the new data write to a new pool region without affecting the data set of any other objects that share the same data chunk.
The Pool’s attributes define the way Volumes, Snapshots and Clones are provisioned.
 Understanding Pool’s Capacity¶
Understanding Pool’s Capacity¶
The introduction of data reduction makes the pool capacity management more complex. Data reduction efficiency depends on the nature of the data, therefore it harder to predict the drives capacity needed for each workload.
Capacity metrics to consider:
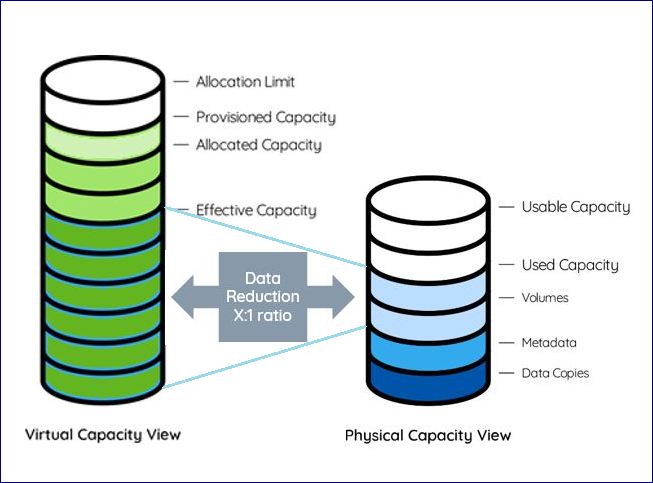
Physical View¶
Raw Capacity - Sum of all drives’ capacities in the Pool
Usable Capacity - Total capacity of all RAID groups in the Pool
Note
the system keeps about 0.5% of each RAID Group capacity as its internal spare
Used by Volumes - Capacity used to store the Volumes data
Used by metadata - Capacity used to store the Pool’s metadata
Used by data copies: - Capacity used to store the snapshots and clones
Used Capacity - The total size of all data written in the Pool
Used Capacity = Used by Volumes + Used by metadatra + Used by data copies
Free Capacity - Available Capacity in the Pool that can be used for new Data and Metadata writes
Free Capacity = Usable Capacity – Used Capacity
%Full = “Used Capacity” / “Usable Capacity”
Note
Capacity alerts are based on Free Capacity
Virtual View¶
Provisioned Capacity - Sum of Pool’s Volumes and Clones capacities as seen by the hosts
Allocated Capacity - Pool’s allocated address space of all Volumes, Snapshots and Clones
Allocation Limit - Max Capacity of the Pool’s address space. Depends on the pool type. See
Free Address Space = Allocation Limit – Allocated Capacity
Data Reduction Saving¶
Thin Provision Ratio = Provisioned Capacity / Effective Capacity
Data Reduction Ratio = Effective Capacity / Used by Volumes
Data Reduction Saving = Effective Capacity - Used by Volumes
Data Reduction Percentage = 1- (1 / Data Reduction Ratio)
e.g.
Data reduction ratio 2:1 , Data Reduction Percentage 50%
Data reduction ratio 5:1 , Data Reduction Percentage 80%
Data reduction ratio 20:1 , Data Reduction Percentage 95%
Pool capacity Monitoring¶
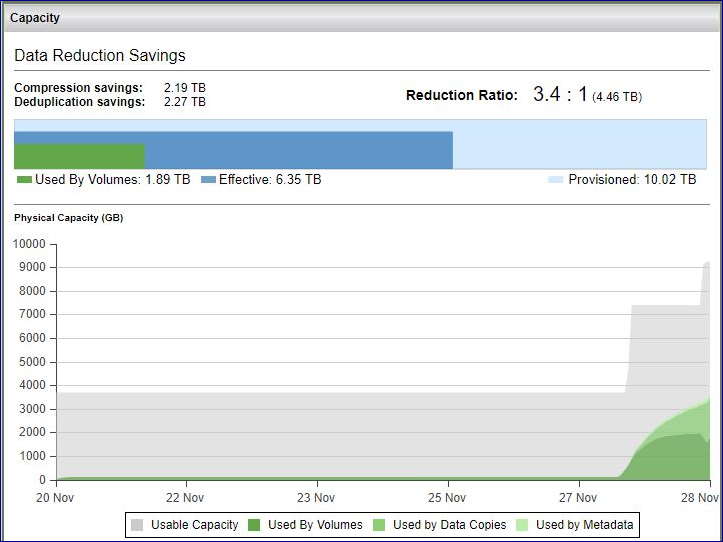
The All Flash VPSA Dashboard show the capacity consumption and data reduction saving
The upper bar shows the current capacity provisioned to the hosts by all pools vs. the effective capacity written by the hosts vs. the physical space needed to store the data.
The lower chart shows trend of time of the physical capacity used and available.
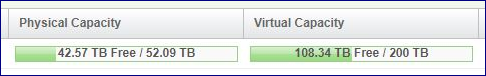
The Pools table shows 2 bars.
The physical capacity bar shows the usable vs. used capacities.
The virtual capacity bar shows the allocated capacity vs. the allocation limit.
<table border=”1” class=”docutils”> <thead> <tr> <th></th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr> <td></td> </tr> </tbody> </table>
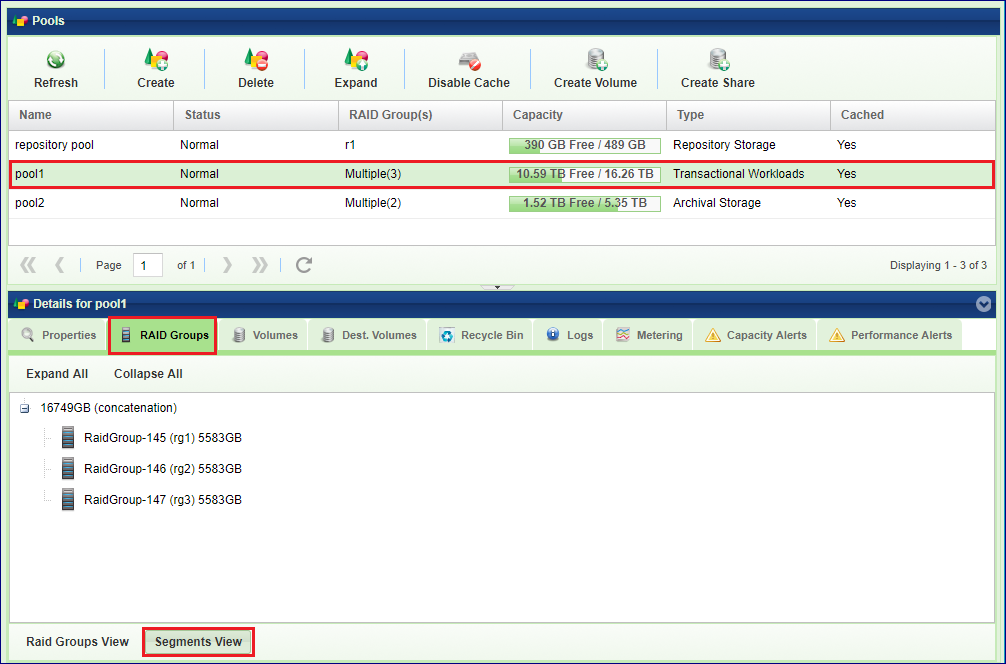
Creating and Managing Pools¶
Creating a Pool¶
Note
By dafault when a a new VPSA is created, a default pool is automatically created for each type of drives selected for this VPSA.
If the default pool does not meet the needs, you can delete it and follow the process described here to create your own pools.
To create a new Storage Pool press either the Create button on the page or the Create Pool button on the page. There are 2 methonds to create a pool.
Create a Pool from RAID Groups
Create a Pool from drives, and the let the system automatically create the needed RAID Groups.
You can toggle between the two by clicking Use Drive Selection / Use RAID Group Selection at the lower left corner of the dialog
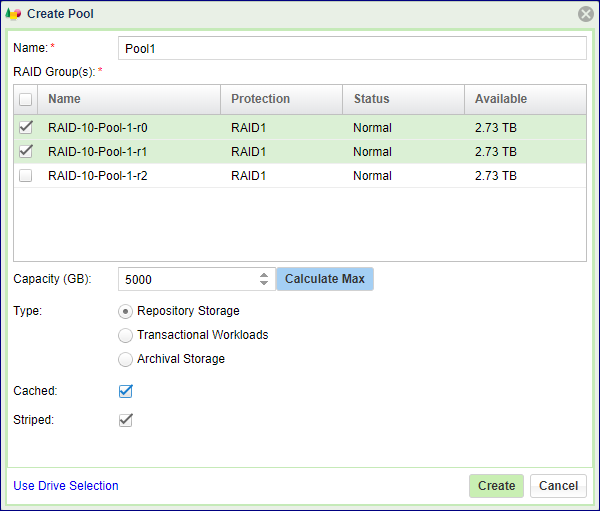
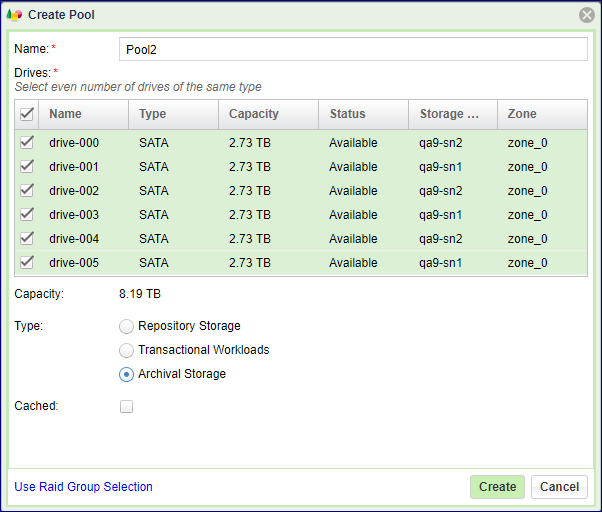
To create a Pool from RAID Groups, you will see the following dialog:
Select the Pool attributes:
Display Name – You can modify this anytime later.
RAID Group(s) selection – Check the box(es) of one or more RAID Groups from which protected storage capacity will be allocated for this Pool.
Capacity – The Pool’s physical capacity shown in GB. By default the capacity is the aggregated capacities of all the selected RAID Groups, but you do not have to allocate full RAID Groups. If you define a capacity smaller than is available in the selected RAID groups the capacity will be evenly distributed between the RAID Groups.
Note
The actual usable capacity of the Pools is a little less than the requested size, as the system reserves some space for the Pool’s metadata (typically up to 100GB).
Type – The VPSA supports Transactional, Repository and Archive Pool types. These Pool types use different chunk sizes for the mapping of virtual LBAs to Physical Drive addresses. The following table describes the tradeoffs for each type and the recommended use cases:
Transactional Pool |
Repository Pool |
Archive Pool |
|
|---|---|---|---|
Chunk size |
256KB |
1MB |
2MB |
Pros |
|
|
|
Cons |
Increased metadata size |
|
|
Use Case |
Transactional Workload with Snapshots |
|
|
Limit |
Transactional Pools have a maximum size of 20TB |
|
|
Transactional Pool |
Repository Pool |
Archive Pool |
|
|---|---|---|---|
Thin Provision Chunk size |
512KB |
1MB |
2MB |
Deduplication Chunk size |
8KB |
16KB |
32KB |
Pros |
|
|
|
Cons |
|
|
|
Use Case |
|
|
|
Limit |
|
|
|
In case there are number of pools in a given VPSA, there is a limit to aggragated total size of all pools. The following table lists the capacity limits of all pools per each VPSA All Flash engine:
Pool Type Engine |
F800 |
F1200 |
F2400 |
F3600 |
F4800 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Transactional |
20 |
40 |
60 |
80 |
100 |
Repository |
40 |
60 |
100 |
160 |
200 |
Archival |
60 |
100 |
160 |
200 |
250 |
Cached – Check this box to use SSD to Cache Server’s reads and writes.
All Pools that are marked as “Cached” share the VPSA Cache.
Flash cache usually improves the performance of volumes based on HDD’s pools. However it depends on the specific workload and the size of the cache vs. the size of the active data set.
If the Pool consists of SSD drives this option will be disabled.
Striped – This check box is enabled only when you select two or more RAID Groups. Striping over RAID-1 or RAID-6 creates RAID-10 or RAID-60 configurations respectively. Use striping to improve performance of random workloads since the IOs will be distributed and all drives will share the workload.
All Flash Array pools are always striped, and this checkpoint is hidden.
To create a Pool from Drives, you will see the following dialog:
The parameters are same as above. Just Check the box(es) of drives that will be allocated for this Pool.
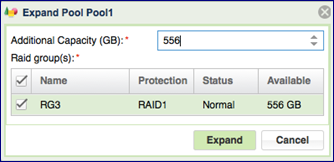
Expanding Pool Capacity¶
To Expand the Pool press the Expand button on the page.
You can use capacity from any RAID Group to expand a Pool. If the RAID Group from which the new capacity is added doesn’t match the protection type or drive type of the existing capacity you’ll see a warning message pop up asking you to confirm the mismatch. Keep in mind that continuing with the mismatched types may impact the pool performance and protection QoS.
 Shrinking Pool Capacity¶
Shrinking Pool Capacity¶
Note
Pool shrink is only supported in All Flash VPSAs.
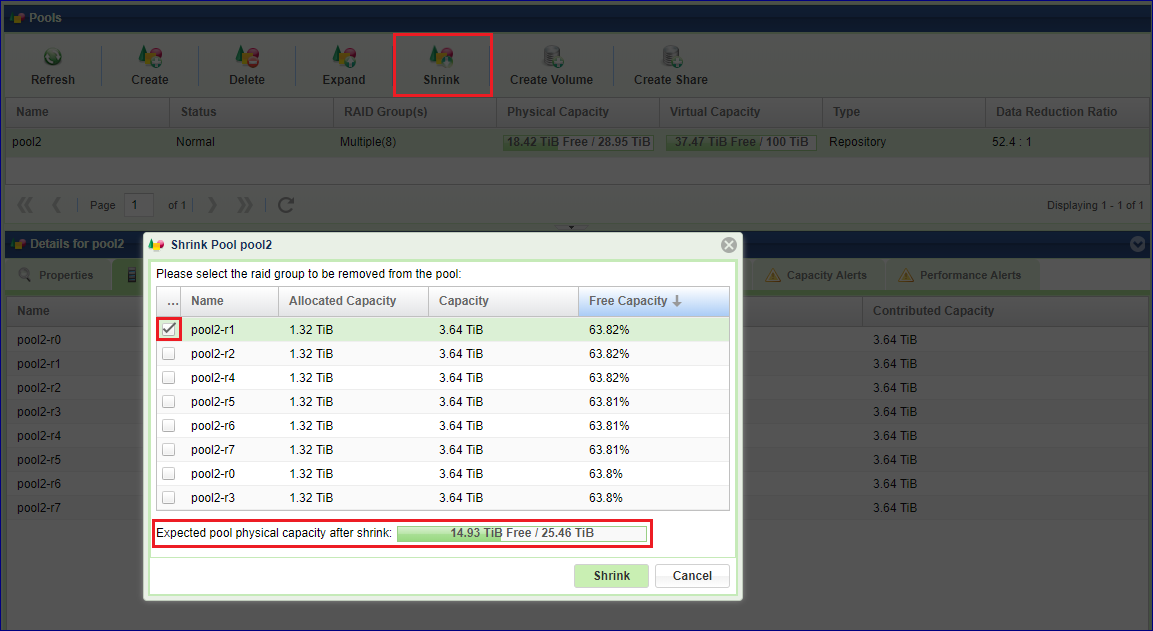
If the pool capacity is not fully used you can shrink it’s size by removing RAID Group(s) (one at a time) from the Pool. The VPSA will evacuate the selected RAID Group and will return the RAID Group to the VPSA for reuse, or for the RAID group to be deleted and the drives removed from the VPSA. To Shrink the Pool press the Shrink button on the page.
Select the RAID Group to remove from the Pool. Check the physical size expected after the shrinking operation is completed, and press Shrink The operation might take a while, depending on the amount of data to be copied to other drives. The system will generate Event once done.
It is possible to enable Caching on non-cached Pools.
One use case for leveraging this capability is to enable caching only after the initial copy of the data into the VPSA. The initial copy typically generates a sequential write IO workload, where non-cached Pools are most efficient. Once the initial copy is completed enable caching on the Pool if you expect a more random type of IO workload.
 Disabling SSD cache on a pool¶
Disabling SSD cache on a pool¶
By default every pool is cached by the VPSA’s SSD cache, but it is also possible to disable caching on cached Pools which will remove this feature. The Enable Cache/Disable Cache buttons toggle depending on the current caching state of the Pool.
Viewing Pool properties¶
The Pools details are shown in the following South Panel tabs:
Properties
 Each Pool of Storage Array includes the following properties:
Each Pool of Storage Array includes the following properties:
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
ID |
An internally assigned unique ID. |
Name |
User assigned name. Can be modified anytime. |
Comment |
User free text comment. Can be used for labels, reminders or any other purpose |
Status |
|
Capacity |
Total available capacity for user data & system metadata. |
Available Capacity |
Available (free) capacity to be used for User data. VPSA reserves 2% of the total Pool capacity for system metadata. If the VPSA needs more capacity for the metadata (very rare scenario), it will be consumed from the available capacity. |
Metadata Capacity |
Metadata Capacity |
Capacity State |
See Managing Pool Capacity Alerts for more details. |
Mode |
|
Type |
|
Stripe Size |
Applicable only for Pools of Striped mode (i.e. when data is striped between 2 or more RAID groups). The Stripe size is always 64KB. |
Cached |
Yes/No – Indicates whether the Pool utilizes SSD for read/write caching |
Cache COW Writes |
Yes/No – Indicates whether flash cache is used for internal snapshots Copy-On-Write Operations.Enabled by default. Disable only on rare cases where frequent snapshots cause extreme load of metadata operations. Consult Zadara support. |
Raid Group(s) |
RAID Group name, or “Multiple (X)” where X denotes the number of RAID Groups in the Pool. |
Created |
Date & time when the object was created. |
Modified |
Date & time when the object was last modified. |
 Each Pool of All Flash Array includes the following properties:
Each Pool of All Flash Array includes the following properties:
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
General |
|
ID |
An internally assigned unique ID. |
Name |
User assigned name. Can be modified anytime. |
Comment |
User free text comment. Can be used for labels, reminders or any other purpose |
Status |
|
Type |
|
Raid Group(s) |
RAID Group name, or “Multiple (X)” where X denotes the number of RAID Groups in the Pool. |
Created |
Date & time when the object was created. |
Modified |
Date & time when the object was last modified. |
Physical Capacity |
|
Usable Capacity |
Total capacity of all RAID groups in the Pool |
Used Capacity |
The total size of all data written in the Pool Used Capacity = Used by Volumes + Used by metadatra + Used by data copies |
Used by Volumes |
Capacity used to store the Volumes data |
Used by Data Copies |
Capacity used to store Snapshots and Clones |
Used by Metadata |
Capacity used to store the Pool’s metadata |
Free Capacity |
Available Capacity in the Pool that can be used for new Data and Metadata writes |
Physical Capacity State |
See Managing Pool Capacity Alerts for more details. |
Virtual Capacity |
|
Provisioned Capacity |
Sum of Pool’s Volumes and Clones capacities as seen by the hosts |
Allocated Capacity |
Pool’s allocated address space of all Volumes, Snapshots and Clones |
Effective Capacity |
Amount of data written in the pool by all volumes and can be accessed by hosts. Not including space taken by snapshots |
Virtual Capacity State |
See Managing Pool Capacity Alerts for more details. |
Capacity Savings |
|
Data Reduction Ratio |
Capacity savings by all data reduction techniques. Data Reduction Ratio = Effective Capacity / Used by Volumes |
Deduplication Ratio |
Capacity savings by deduplication |
Compression Ratio |
Capacity savings by compression |
Thin Provision Ratio |
Capacity savings by thin provisioning technique. Thin Provision Ratio = Provisioned Capacity / Effective Capacity |
RAID Groups
In the This tab lists the RAID Groups allocated to the selected Pool. Each RAID Group includes the following information:
Name
Protection (RAID-1, RAID-5or RAID-6)
Status
Contributed Capacity
In the This tab shows the structure of pool made of concatinated or striped segments
Volumes and Dest Volumes
These two tabs display the provisioned Volumes and the Provisioned Remote Mirroring Destination Volumes. Please note that the Dest Volumes are not displayed in the main page since most operations are not applicable to them. Displaying the list of the Dest Volumes in the Pools South Panel provides a complete picture of the Objects that consume capacity from the Pool. Each Volume includes the following information:
Name
Capacity (virtual, not provisioned)
Status
Data Type (Block or File-System)
Recycle Bin
By default when you delete a volume it moves to a Pool’s Recycle Bin for 7 days until it is permanently deleted. From the Recycle Bin an administrator can purge (permanently delete) or restore a volume.
Logs
Displays all event logs associated with this Pool.
Metering
The Metering Charts provide live metering of the IO workload associated with the selected Pool.
The charts display the metering data as it was captured in the past 20 “intervals”. An interval length can be set to one of the following: 1 Second, 10 seconds, 1 Minute, 10 Minutes, or 1 Hour. The Auto button lets you see continuously-updating live metering info (refreshed every 3 seconds).
Pool Metering includes the following charts:
Chart |
Description |
|---|---|
IOPs |
The number of read and write SCSI commands issued to the Pool, per second. |
Bandwidth (MB/s) |
Total throughput (in MB) of read and write SCSI commands issued to the Pool, per second. |
IO Time (ms) |
Average response time of all read and write SCSI commands issued to the Pool, per selected interval . |
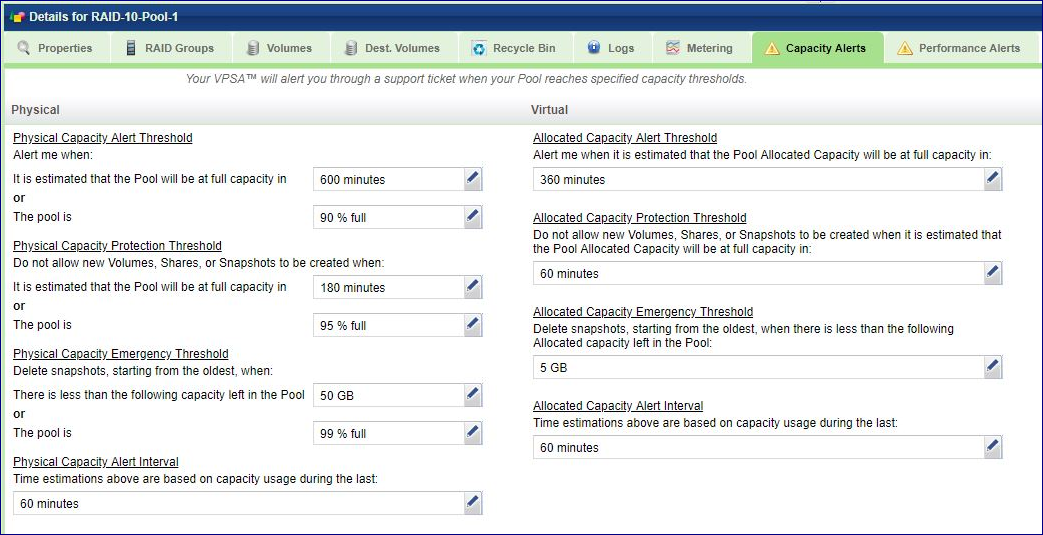
Capacity Alerts
The Capacity Alerts tab lists the configurable attributes of the Pool Protection Mechanism. See Managing Pool Capacity Alerts for more details. You can modify the following attributes:
Physical Pool Alert Mode Threshold - “Alert me when it is estimated that the Pool will be at full physical capacity in X Minutes.”
Default Value: 360 minutes
Physical Pool Protection Mode Threshold - “Do not allow new Volumes, Shares, or Snapshots to be created when it is estimated that the Pool will be at full physical capacity in X Minutes.”
Default Value: 60 minutes
Physical Pool Calculation Window - “Calculate the estimated time until the Pool is full based on new capacity usage in the previous X minutes.”
Default Value: 60 minutes
Physical Pool Emergency Mode Threshold - “Delete snapshots, starting from the oldest, when there is less than the following physical capacity left in the Pool”
Default Value: 50 GB
Allocated Capacity Alert Mode Threshold - “Alert me when it is estimated that the Pool’s address space will be at full capacity in X Minutes.”
Default Value: 360 minutes
Allocated Capacity Protection Mode Threshold - “Do not allow new Volumes, Shares, or Snapshots to be created when it is estimated that the Pool’s address space will be at full capacity in X Minutes.”
Default Value: 60 minutes
Allocated Capacity Calculation Window - “Calculate the estimated time until the Pool’s address space is full based on new capacity usage in the previous X minutes.”
Default Value: 60 minutes
Allocated Capacity Emergency Mode Threshold - “Delete snapshots, starting from the oldest, when there is less than the following free address space left in the Pool”
Default Value: 5 GB
Performance Alerts
The Performance Alerts tab lists the Pool’s ability to send alerts when performance drops below expectations. See Managing Pool Performance Alerts for more details.
Managing Pool Capacity Alerts¶
The VPSA’s efficient and sophisticated storage provisioning infrastructure maximizes storage utilization, while providing key enterprise-grade data management functions. As a result, you can quite easily over-provision a Pool with Volumes, Snapshots and Clones, hence requiring a Pool Protection Mechanism to alert and protect when free Pool space is low.
The VPSA Pool Protection Mechanism is either time-based or capacity consumption based. The goal is to provide you sufficient time to fix the low free space situation by either deleting unused Volumes/Snapshots/Clones or by expanding the Pool’s available capacity (a very simple and quick process due to the elasticity of the VPSA and the Zadara Storage Cloud).
The VPSA measures the rate at which the Pool’s free space is consumed and calculates the estimated time left before running out of free space.
The following user-configurable parameters impact alerts and operations that are performed as part of the Pool Protection mechanism:
Physical Pool Capacity Alert Threshold – The estimated time (in minutes) before running out of free space or percentage used. When triggered an online support ticket is submitted and an email is sent to the VPSA user. When crossing this threshold the Free Capacity State changes to “Alert” and the available capacity will be shown in Yellow. A secondary “reminder” ticket and an email will be generated when only half of this threshold’s estimated time is left.
Default time: 600 minutes (10 hours)
Minimum: 1 minute (0 means disable this alert by time)
or
Default Percentage: 90% full
Minimum: 1 % (0 means disable this alert by %)
Physical Pool Capacity Protection Threshold – The estimated time (in minutes) before running out of free space. When triggered the VPSA starts blocking the creation of new Volumes, Snapshots and Clones in that Pool. A support ticket and email are also generated. When crossing this threshold, the Free Capacity State changes to “Protect” and the available capacity will be shown in Red.
Default: 180 minutes (3 hour)
Minimum: 1 minute (0 means disable this alert by time)
or
Default Percentage: 95% full
Minimum: 1 % (0 means disable this alert by %)
Physical Pool Capacity Emergency Threshold – When the Pool’s free capacity drops below this fixed threshold (in GB) or below the specified % threshold, the VPSA starts freeing Pool capacity by deleting older snapshots. The VPSA will delete one snapshot at a time, starting with the oldest snapshot, until it exceeds the Emergency threshold (i.e. when free capacity is greater than the threshold). A support ticket and email are also generated. When this threshold is crossed the Free Capacity State changes to “Emergency” and the available capacity will be shown in Red.
Default: 50 GB
Minimum: 1 GB
or
Default Percentage: 99% full
Minimum: 1 % (0 means disable this alert by %)
Physical Pool Capacity Alert Interval - The size of the window (in minutes) that is used to calculate the rate at which free space is consumed. The smaller the window is the more this rate is impacted by intermediate changes in capacity allocations, which can result from changes in workload characteristics and/or the creation/deletion of new Snapshots and Clones.
Default: 60 minutes (1 hours)
Minimum: 1 minute
 In addition to the physical capacity alerts, The All Flash VPSA provides alerts in case
The Pool allocation (virtual address space) is near capacity.
In addition to the physical capacity alerts, The All Flash VPSA provides alerts in case
The Pool allocation (virtual address space) is near capacity.
Free Address Space = Allocation Limit – Allocated Capacity
The following user-configurable parameters impact alerts and operations that are performed as part of the Pool Protection mechanism:
Allocated Capacity Alert Threshold – The estimated time (in minutes) before running out of free address space. When triggered an online support ticket is submitted and an email is sent to the VPSA user. When crossing this threshold the Allocated Capacity Alert Mode changes to “Alert” and the available address sace will be shown in Yellow. A secondary “reminder” ticket and an email will be generated when only half of this threshold’s estimated time is left.
Default: 360 minutes (6 hours)
Minimum: 1 minute (0 means disable this alert)
Allocated Capacity Protection Threshold – The estimated time (in minutes) before running out of free address space. When triggered the VPSA starts blocking the creation of new Volumes, Snapshots and Clones in that Pool. A support ticket and email are also generated. When crossing this threshold, the Allocated Capacity Alert Mode changes to “Protect” and the available address space will be shown in Red.
Default: 60 minutes (1 hour)
Minimum: 1 minute (0 means disable this alert)
Allocated Capacity Alert Interval - The size of the window (in minutes) that is used to calculate the rate at which free address space is consumed. The smaller the window is the more this rate is impacted by intermediate changes in capacity allocations, which can result from changes in workload characteristics and/or the creation/deletion of new Snapshots and Clones.
Default: 60 minutes (1 hours)
Minimum: 1 minute
Allocated Capacity Emergency Threshold – When the Pool’s free address space drops below this fixed threshold (in GB), the VPSA starts freeing Pool capacity by deleting older snapshots. The VPSA will delete one snapshot at a time, starting with the oldest snapshot, until it exceeds the Emergency threshold (i.e. when free address space is greater than the threshold). A support ticket and email are also generated. When this threshold is crossed the Free Capacity State changes to “Emergency” and the available address space will be shown in Red.
Default: 5 GB
Minimum: 1 GB
Managing Pool Performance Alerts¶
A VPSA administrator has the option to set Pool Performance Alerts in addition to the default Pool Capacity Alerts. Performance Alerts are available for:
Read IOPS Limit – Creates an alert when the average read IOPS, during the past minute, for a Pool exceeds a user-specified threshold.
Read Throughput Limit - Creates an alert when, during the past minute, the average read MB/s for a Pool exceeds a user-specified threshold.
Read Latency Limit – Creates an alert when, during the past minute, the average read latency for a Pool exceeds a user-specified threshold.
Write IOPS Limit – Creates an alert when, during the past minute, the average write IOPS for a Pool exceeds a user-specified threshold.
Write Throughput Limit - Creates an alert when, during the past minute, the average write MB/s for a Pool exceeds a user-specified threshold.
Write Latency Limit – Creates an alert when, during the past minute, the average write latency for a Pool exceeds a user-specified threshold.