Managing Virtual Private Storage Arrays¶
Virtual private storage array instances running in the cloud can be centrally managed and monitored by cloud admins from Command center. Command center VPSA management feature set provides administrators with a single pain of glass in which the receive a holistic image of the underlying instances status and operations and allows for enforcements of policies , lifecycle management and supervised resource distribution.
Viewing Virtual Private Storage Array Properties¶
Specific VPSAs can be reached by clicking on the VPSAs label on Command centers left menu panel and selecting the appropriate Instance from the displayed list. The VPSA main dashboard tab provides information regarding its configuration, current health status and network topology.
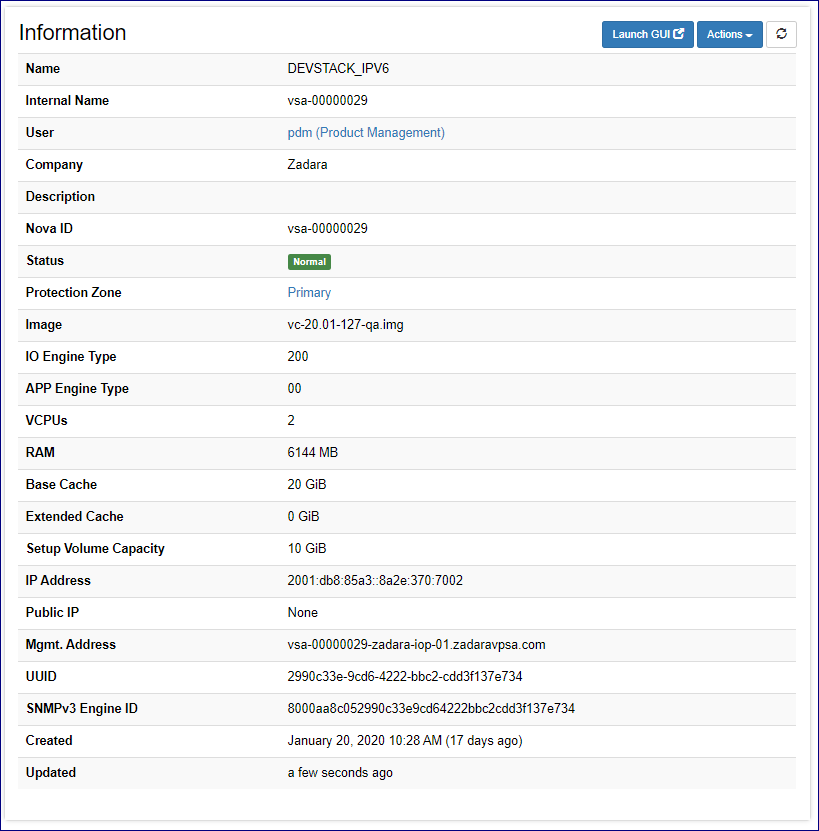
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Instance display name |
Internal Name |
internal instance name |
Company |
Creating user company |
Description |
Description given while instance was provisioned |
Nova ID |
Nova ID for this instance |
Status |
Current Instance status |
Protection Zone |
Instance protection zone configuration |
Image |
Instance deployment image |
IO Engine Type |
VPSA IO Engine Flavor |
App Engine Type |
VPSA APP Engine Flavor |
VCPUs |
Instance VCPU count |
RAM |
Instance Configured RAM capacity |
Base cache |
Instance Base Cache capacity |
Extended Cache |
Instance Extended SSD cache configured capacity |
Setup Volume Capacity |
Instance setup volume capacity |
IP Address |
Instance Floating frontend IP address |
Public IP |
Instance public IP address |
Mgmt. Address |
Instance hostname for management access |
UUID |
Instance UUID |
SNMPv3 Engine ID |
Instance SNMPv3 EngineID |
Created |
Creation timestamp |
Updated |
Last update timestamp |
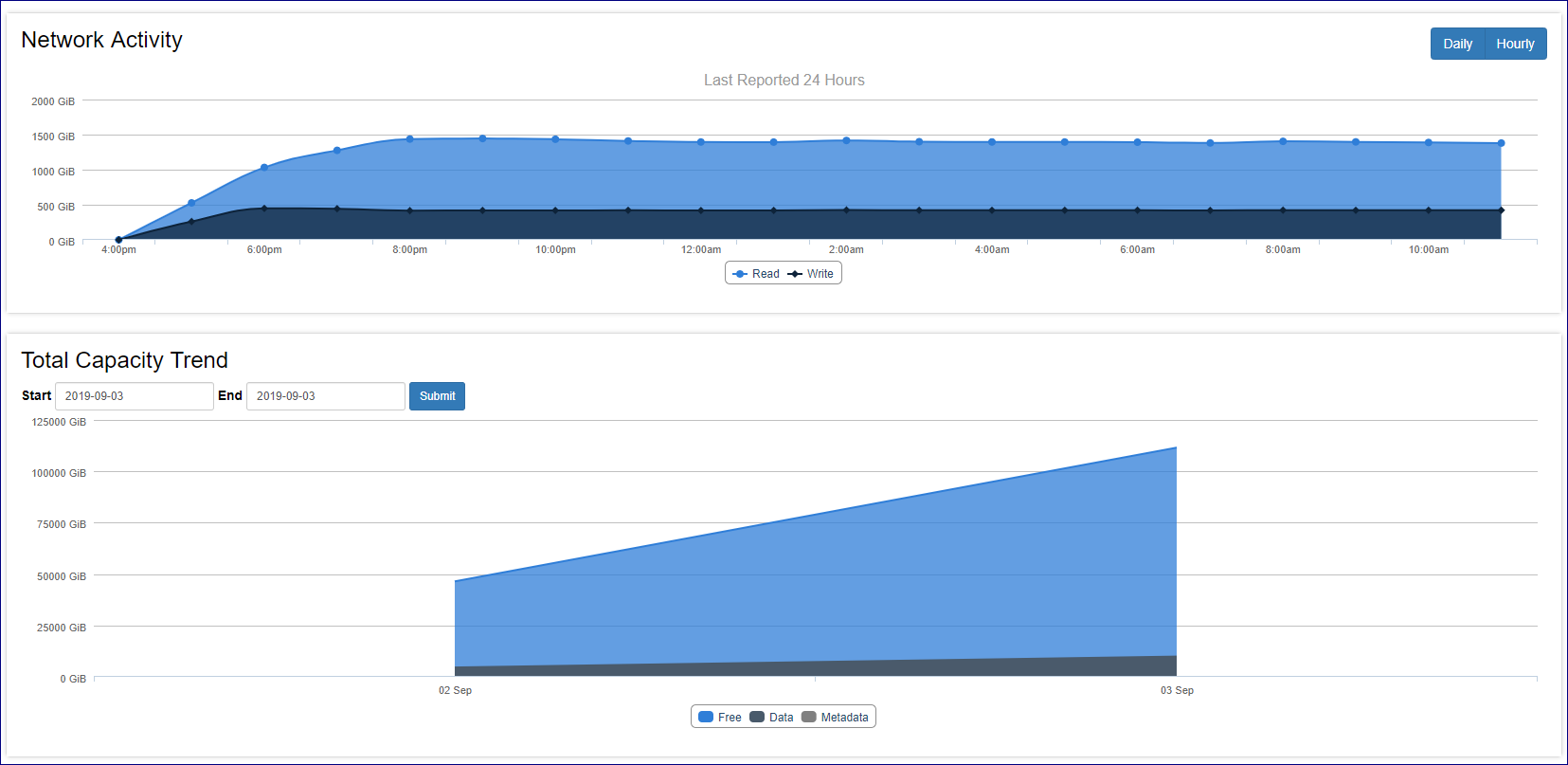
The main dashboard also contains monitoring charts regarding the VPSA capacity utilization and Network activity.
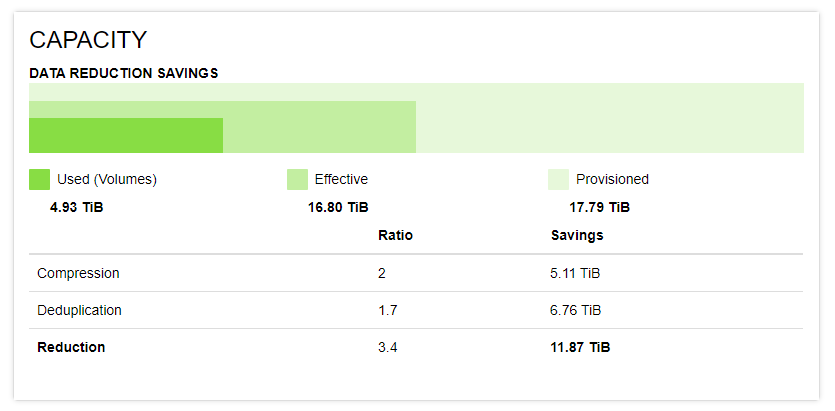
For VPSA Flash array the main dashboard also contains a data reduction savings chart presenting used capacity vs. provisioned and effective capacity. The Flash Array Data reduction tile also includes information about savings from inline data deduplication and inline data compression and the VPSA overall data reduction ratio.
The VPSA resource tabs provides information regarding underlying resources attached to the VPSA:
Physical drives
Virtual controllers
RAID groups
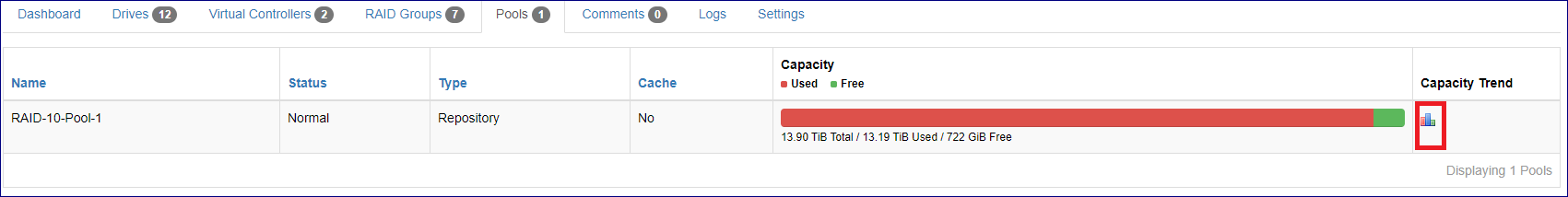
Pools
Note
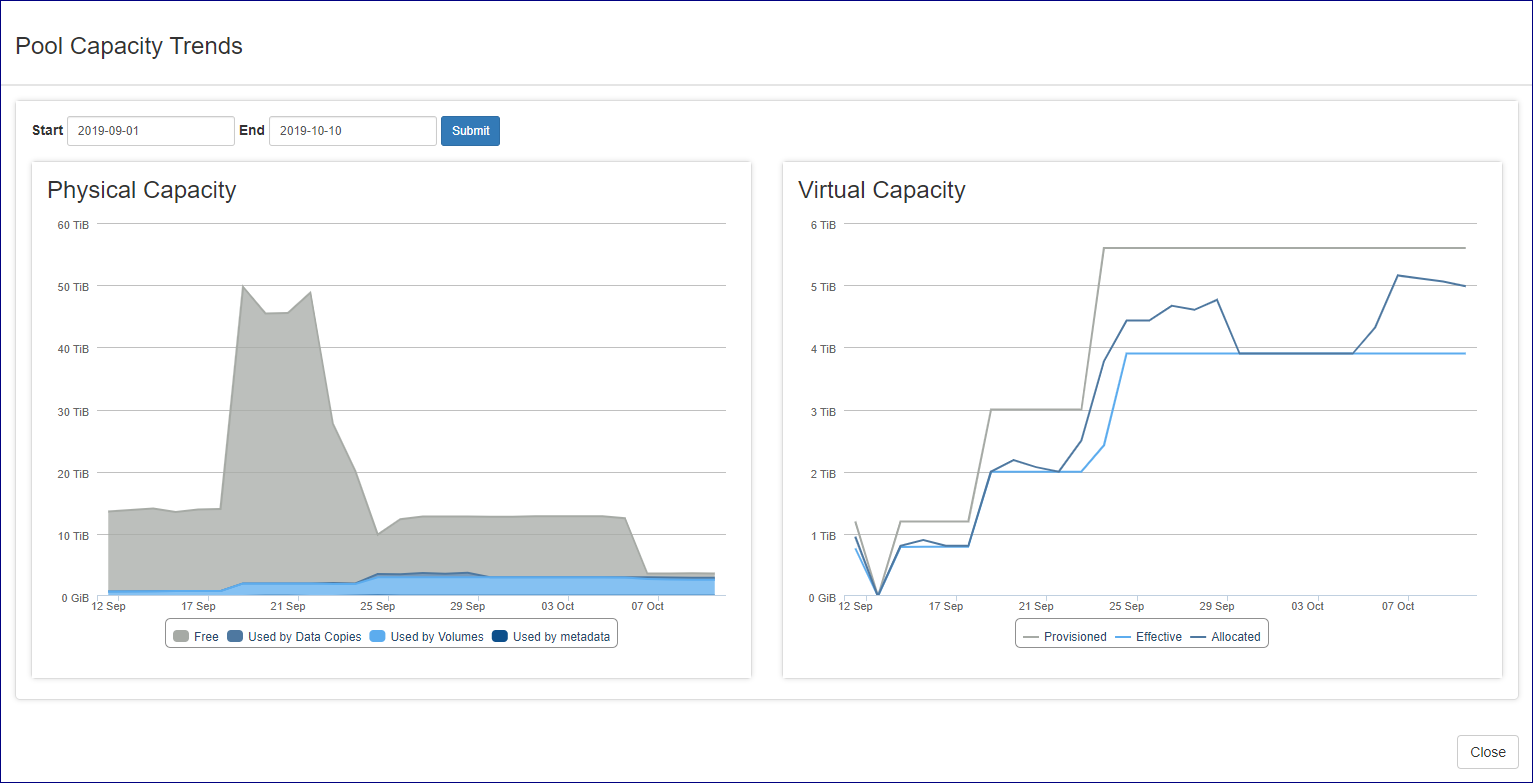
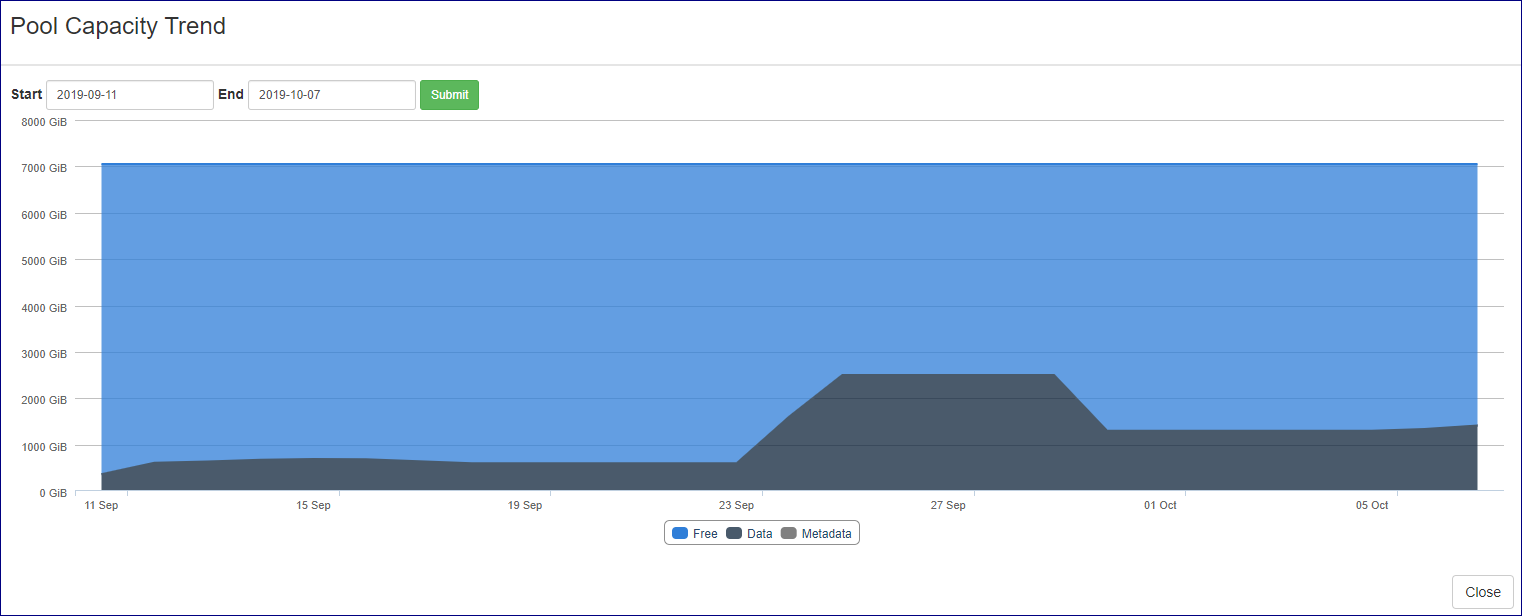
The VPSA Pools tab contains pool capacity consumption trend charts that provides cloud administration with an overview of the pools capacity change over time and the effect of data reduction mechanisms such as deduplication and compression on all flash VPSA pools. To present the capacity trend for a specific pool navigate to the VPSA pools tab, select the required pool and click on the relevant chart icon on the capacity trend column.
The pool capacity charts display differs between a hybrid VPSA and a Flash VPSA:
An all flash VPSA pool capacity trend display contains 2 charts:
Overall pool capacity trend over time
Provisioned capacity vs. virtual capacity and effective capacity over time
A hybrid VPSA pool capacity trend contains only the Overall pool capacity trend over time chart.
Configuring Virtual Private Storage Array Settings¶
To view or alter VPSA settings click on the Settings tab on the VPSA dashboard.
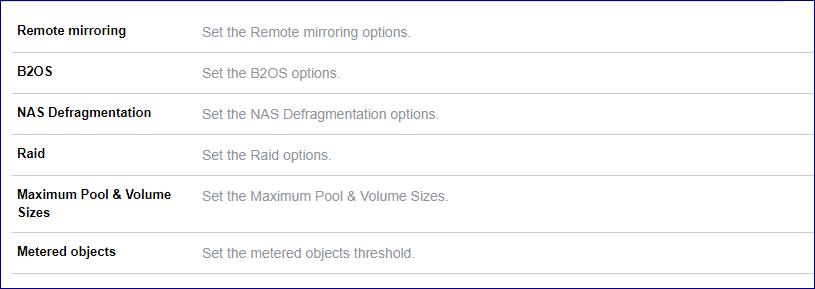
Remote mirroring properties
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Dst total quota pc |
Allowance for amount of unapplied data for all VPSA mirror jobs 0 - No quota enforcement |
Connections count |
Number of TCP sessions established between two VPAs performing mirroring |
Backup to object storage(B2OS)
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Src buffers count |
Amount of source buffers allocated for B2OS activities |
Dst buffers count |
Amount of destination buffers allocated for B2OS activities |
NAS defragmentation
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Minimum extents count |
Amount of extents a file needs to have to be considered for defragmentation |
RAID
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Allow mixed types |
Is HDD type mixture in RAID group/pool allowed? |
RAID6 max drives |
Maximum members in a RAID-6 group |
Maximum Pool & Volume Sizes
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Pool repository max size |
Maximum capacity(TB) of a repository pool |
Pool transactional max size |
Maximum capacity(TB) of a transactional pool |
Pool archival max size |
Maximum capacity(TB) of a archival pool |
Maximum Pool & Volume Sizes
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Check interval |
Interval in seconds for validation of metered objects threshold alerts |
Report interval |
Interval in seconds for rate limiting all metered objects thresholds alerts |
Read cache late IO threshold |
Amount of read hit IO operations with late time exception required to trigger an alert |
Read cache late IO threshold time(ms) |
Read hit IO operation service time value that is considered as late IO |
Write cache late IO threshold |
Amount of write hit IO operations with late time exception required to trigger an alert |
Write cache late io threshold time (ms) |
Write hit IO operation service time value that is considered as late IO |
Enable metering upload agent |
Enable upload of metering data to an external cloud repository |
Ticket Settings Please go to Managing Cloud Settings Management settings section in this manual for details regarding the ticket settings section
Performing Virtual Private Storage Array Operations¶
Changing VPSA engine configuration
Command center can be used to modify a VPSA engine type (to a bigger or smaller engine) and to add or change configuration of a VPSA ZCS engine.
To change engine configuration click on the actions button from the VPSA dashboard and select Change Engine Type(s) from the drop down menu.
In the popup window that will appear select the type of VPSA engine you would like to shift to and/or the type of ZCS engine.
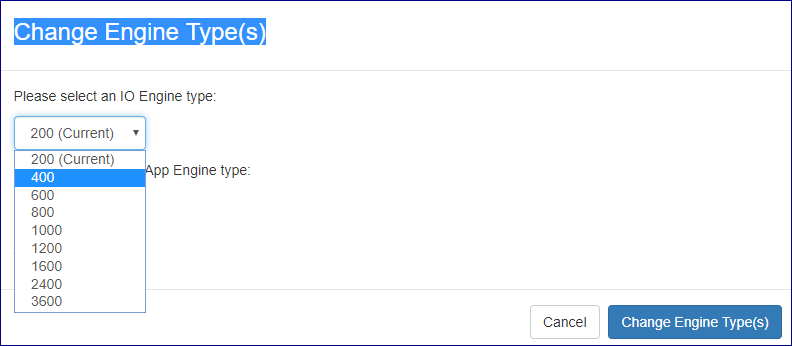
You can also configure advanced option for the model change process by clicking on Advanced options
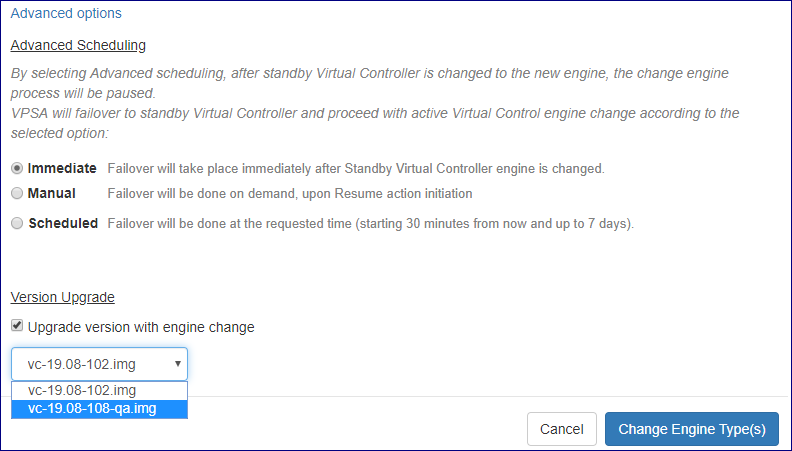
option |
Description |
|---|---|
Advanced scheduling |
Configure when does the engine change process performs required
virtual controller failover:
|
Version upgrade |
Perform VPSA version upgrade alongside the engine model change process |
Click on the Change Engine Type(s) button to proceed and approve the operation in the popup windows that will appear.
The engine reconfiguration process will commence and your VPSA status will be modified to change engine and will be remodified to Normal as the process
concludes.
Adding physical drives
To add physical drives to a VPSA click the Actions button then select Add drives from the drop down menu.
On the popup dialog that will appear select the number of drives to be added and the drive type.
Click on the Add drives button, the request will be submitted.
Note
Change VPSA cache configuration
Cloud Administrators can use Command center to change the Flash cache configuration of a VPSA and add/remove Flash cache capacity on top of the specific model baseline.
Note
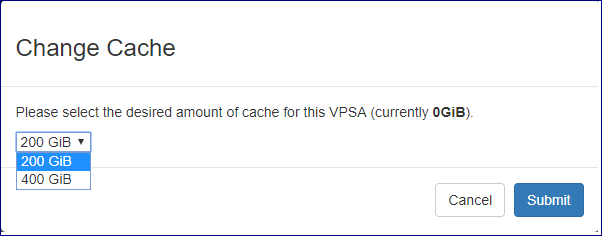
To change cache configuration for a specific VPSA click the Actions button then select Change Cache from the drop down menu.
On the popup dialog that will appear select the new cache configuration you would like to apply for the VPSA and click on the Submit button to confirm.
Upgrading a VPSA
Command center allows administrators to perform version upgrade on the VPSA instances running in the cloud.
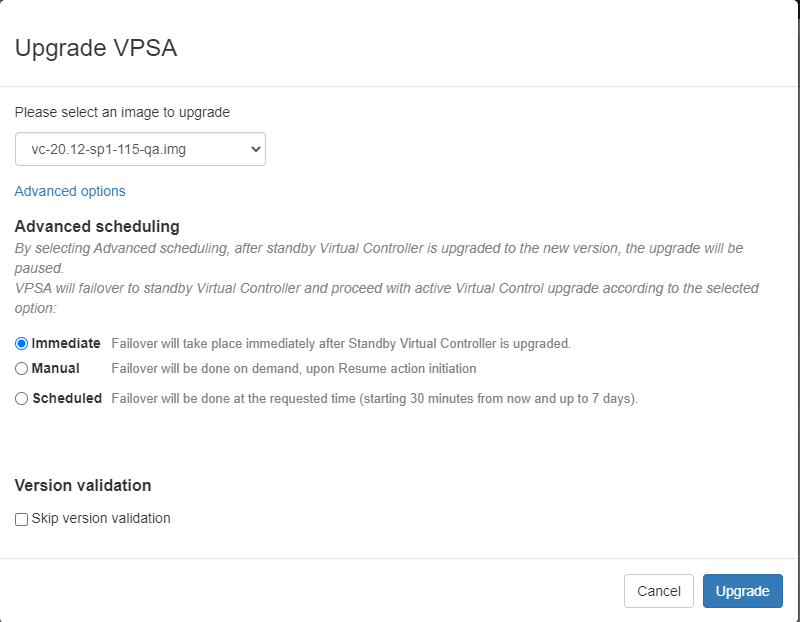
To perform version upgrade click on the Actions button then select Upgrade from the drop down menu.
On the popup dialog that will appear select the specific image level to which you would like to upgrade to.
Advanced options for upgrade can also be selected these options include the ability to schedule the VPSA upgrade and perform an manual VPSA upgrade ( failover performed manually by admin).
You can also request that version checking will be skipped in the upgrade process.
to finalize selection click on the Upgrade button .
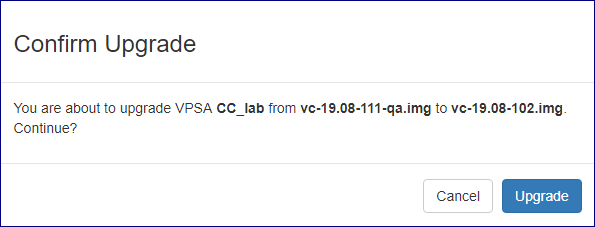
Another Pop up dialog will appear requesting confirmation for upgrading to the selected version click on the Upgrade button to confirm the process.
The request will be submitted and the VPSA status property will change to Upgrading version while the process is running.
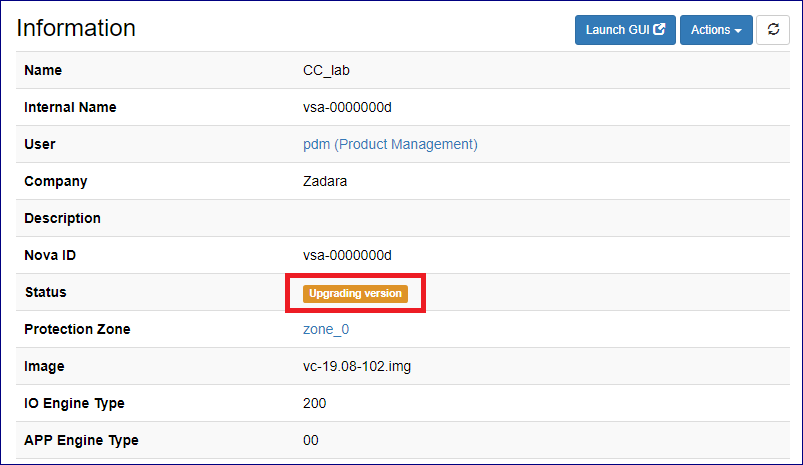
When the VPSA version upgrade process is completed the status property will be changed back to Normal.
Note
Canceling a Scheduled VPSA upgrade For VPSAs in version 20.12 and above who was set up for a scheduled upgrade operation this scheduled upgrade can be canceled from Command Center.
To cancel a scheduled upgrade click on the Actions button then select Cancel Scheduled upgrade from the drop down menu.
on the popup window that will appear confirm upgrade cancellation and the scheduled upgrade will be canceled.
Note
Assigning a Public IP address to a VPSA
In specific cases where a VPSA needs to be available for management access from outside of his Cloud allocated VLAN, a public IP address can be assigned to it. On information regarding the definition of Cloud level public IP ranges please refer to Creating Public IP addresses in this manual.
To assign a public IP address go to the appropriate object storage instance and click the Actions button
and select assign public IP from the drop down menu.
Note
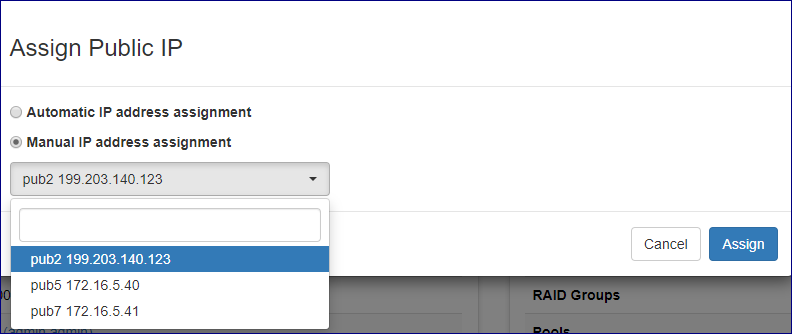
Public IP addresses can be automatically assigned from a cloud level pool or manually selected.
To automatically assign a public IP address: On the popup dialog that will appear make sure Automatic IP address assignment is selected and confirm the operation by clicking on the Confirm button.
To manually select a specific public IP address: On the popup dialog that will appear select Manual IP address assignment, select the required public IP and confirm the operation by clicking on the Confirm button.
Note
Adding\Removing a virtual network to a VPSA
An Existing VSPA is created with one primary virtual network and can be assigned with additional virtual networks. VPSAs connected to multiple networks can be utilized to Enable use cases requiring per volume partitioning/isolation.
To assign a virtual network to a VPSA first make sure that an appropriate virtual network is defined in the cloud (except the one already used by the VPSA).
Click the Actions button and select Add Virtual Network from the drop down menu.
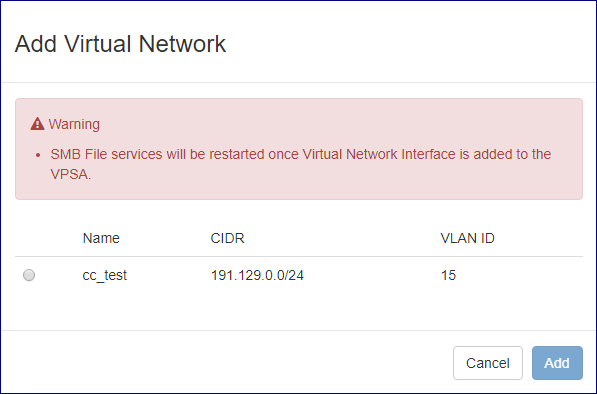
On the popup dialog that will appear select the appropriate virtual network and confirm the operation by clicking on the Add button.
Warning
When the add operation completes the newly added virtual network should be displayed in the VPSA virtual networks tab.
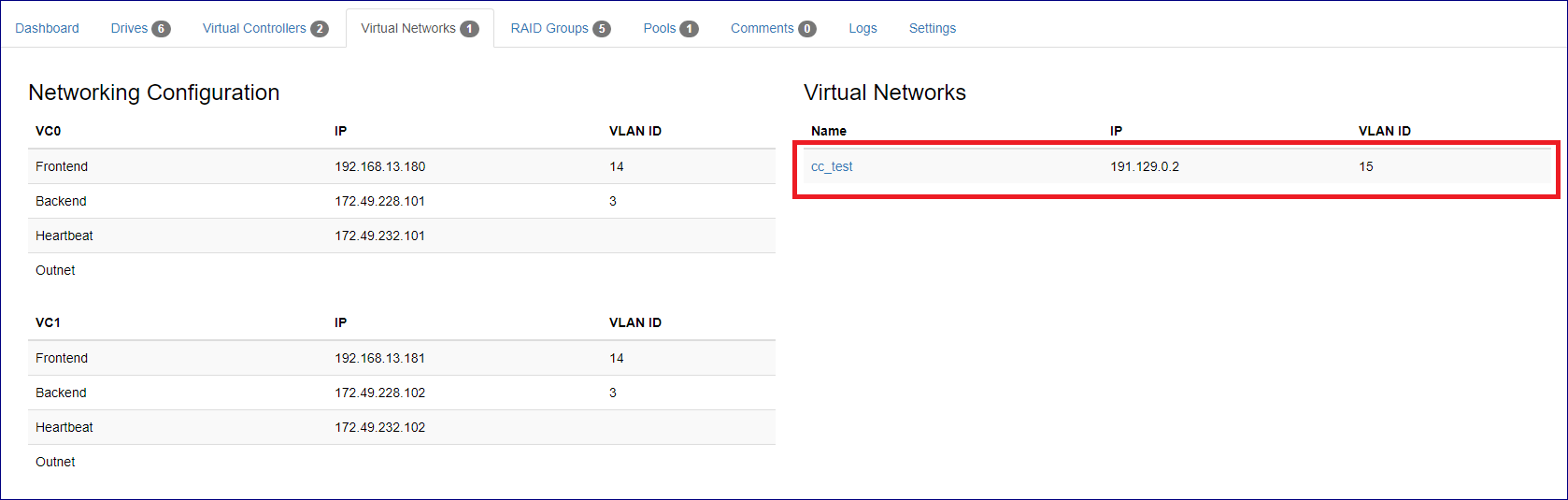
Note
Number of virtual networks per VPSA is limited to 5.
VPSA REST API/GUI is accessible through any virtual networks.
Only Primary virtual networks IP is registered in DNSimple
VPSA can’t have two virtual networks with the same VLAN.
Only “Primary Virtual Network” is a routable network. Remaining virtual networks are not routable.
Active Directory can be joined only through “primary virtual network”.
Backup (B2OS), Mirror, Remote Clone through FE network are only allowed via the “primary virtual network”.
ZCS container services exposed through FE network can be done only on “primary virtual network”.
“iSER” host connectivity is available only on the “Primary Virtual Network”.
To release a virtual network from a VPSA click the Actions button and select Release Virtual Network from the drop down menu.
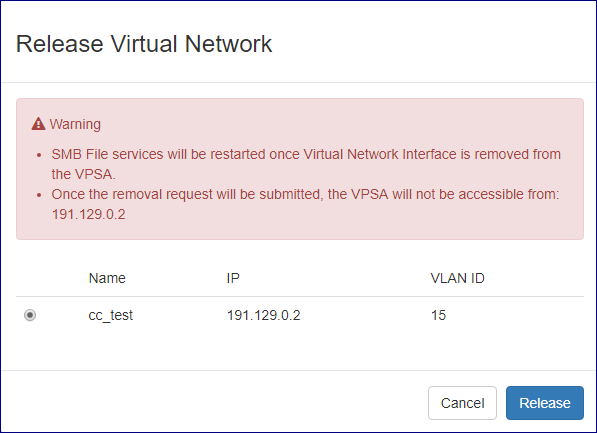
On the popup dialog that will appear select the appropriate virtual network and confirm the operation by clicking on the Release button.
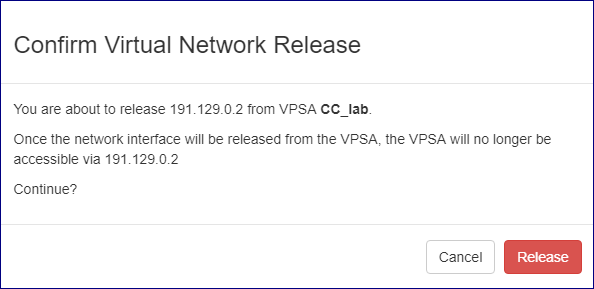
Note
Reconfirm the release operation on the popup dialog that will appear by clicking the red Release button.
Dedicating VPSA to NeoKarm compute cloud
A VPSA can be connected to a NeoKarm compute cloud to be utilized as a backend to a NeoKarm Storage Pool ( used for creation of EBS compatible block volumes for NeoKarm VMs). A VPSA connected to NeoKarm cloud is used solely for this compute cloud and therefore “dedicated” to it.
To dedicate a VPSA to a NeoKarm Compute Cloud click the actions and select Dedicate VPSA to Compute from the drop down menu.
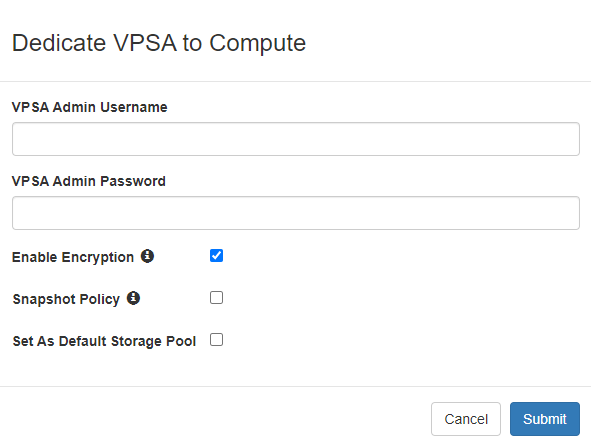
On the popup dialog that will appear provide the following :
An admin username for this VPSA to be used by NeoKarm for VPSA API
The admin user password
You can also toggle :
Volume encryption for the compute cloud block volumes provisioned from this VPSA
The use of VPSA default snapshot policies for the compute cloud block volumes
Whether this VPSA will be attached to the NeoKarm compute cloud default storage pool.
After providing all required information click on submit to confirm dedication of this VPSA .
The operation will commence. If it concludes successfully the VPSA will be marked with a  label.
label.
Releasing a VPSA from NeoKarm compute cloud dedication
A VPSA dedicated to NeoKarm compute cloud can be released from its dedication.
To release a VPSA from compute cloud dedication click the actions and select Release VPSA from Compute from the drop down menu.
On the popup dialog that will appear confirm release by clicking on the submit button.
Performing managed virtual controller failover
Command center can be used to trigger a managed VPSA failover to its standby virtual controller. Managed failover can be used by cloud administrator to evacuate all active virtual controllers from a specific Storage node before infrastructure operations or hardware replacement.
Warning
To perform virtual controller failover click the Actions button and select Failover from the drop down menu.
Failover can be performed immediately or be scheduled to a specific date and time.
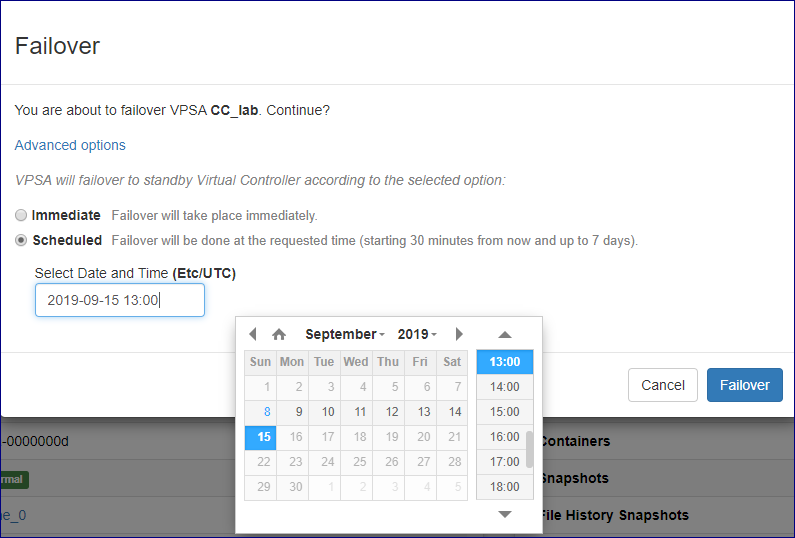
To perform immediate Failover: on the popup dialog that will appear confirm the action by clicking on the Failover button
or click on the advanced settings link and make sure that failover is set to immediate and then click on the Failover button.
To schedule failover to a specific point in time: on the popup dialog that will appear click on the advanced settings and select Scheduled,
select the date and time in which failover should be performed and then click on the Failover button.
The failover process will be initiated, Failover status and progress can be monitored from the VPSA log tab.
Moving a virtual controller
In cases where the cloud Storage Node inventory & capacity are sufficient- virtual controllers can be moved from the SN the currently reside in to another. Both primary and secondary virtual controllers can be moved, moving the primary virtual controller will trigger a failover operation prior to its relocation.
to move a virtual controller failover click the Actions button and select Move Virtual controller from the drop down menu.
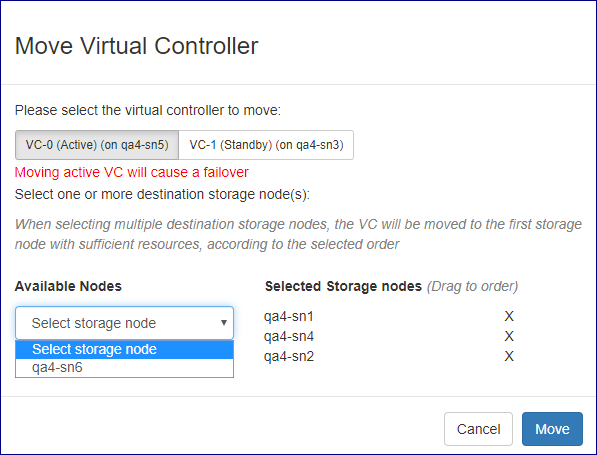
Select the virtual controller you want to relocate and select one or more storage nodes as the destination, in case multiple storage node a slected relocation
will be performed to the first SN that has sufficient resource capacity.
to confirm relocation click on the Move button.
Note
Hibernate a VPSA
VPSA Hibernation will take the instance offline and free its consumed resources ( vCPU , RAM ) on the Storage Nodes level. Hibernation of a VPSA will also reduce its associated service cost. For VPSA in a hibernated state only drives are billed. Hibernating a VPSA involves the process of deleting its Virtual Controllers (the VPSA) while maintaining the data drives and all the necessary metadata to resume its operation at a later stage. Resuming a hibernated VPSA only takes a few minutes.
To hibernate a VPSA click the Actions button and select Hibernate from the drop down menu. On the popup dialog that will appear
Type HIBERNATE on the textbox item as required and confirm the operation by clicking on the Hibernate button.
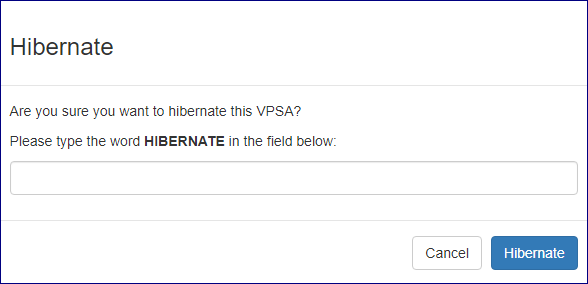
The request will be submitted for processing, upon successful completion the VPSA status will change to Hibernated.
Creating VPSA Zsnap
To Trigger Manual creation of Zsnap for a VPSA go to its dashboard, click the Actions button and select Create Zsnap from the drop down menu.
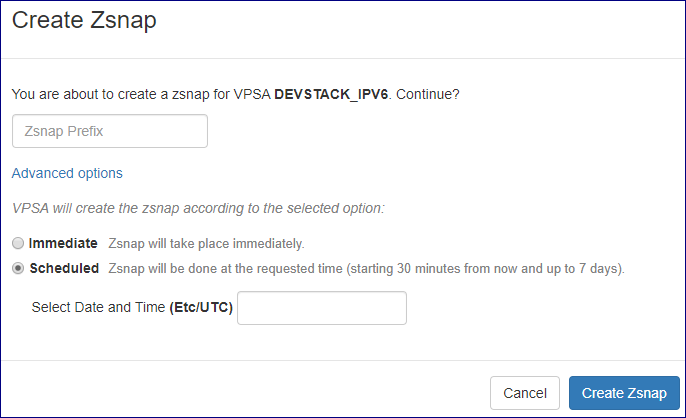
VPSA Zsnaps can be created immediately or scheduled.
To create Zsnap immediately: On the popup dialog that will appear provide the prefix for the Zsnap and confirm creation by clicking on the Create Zsnap button.
To schedule a Zsnap creation: On the popup dialog that will appear provide the prefix for the Zsnap and click on Advanced option. select Scheduled Zsnap and provide
creation date and time. to confirm scheduling the Zsnap click on the Create Zsnap button.
Purging\Restoring a deleted VPSA
Any VPSA instance that has been deleted from the cloud will remain in the clouds recycle bin for a period specified in it’s settings (see Managing Cloud Settings). Cloud administrator can manually purge a deleted VPSA prior to the recycle bin retention period expiration to free cloud resources allocated by it (Physical drives). Administrator can also restore the VPSA from the recycle bin and get it up and running on the same data set it contained as it was deleted.
To purge a VPSA from the clouds recycle bin make sure the status of the VPSA is Recycle bin , click the Actions button
then select Purge from the drop down menu. Type the VPSA ID specified in the popup dialog that will appear and click on the Purge button to confirm the operation.
To restore a VPSA from the clouds recycle bin make sure the status of the VPSA is recycle bin , click the Actions button
then select Restore from the drop down menu. On the popup dialog that will appear click on the Restore button to confirm the operation. The restoration will start and the VPSA status will be modified
to Lunching and reverted back to Normal as the restoration concludes.